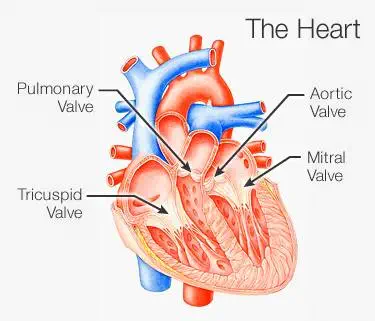
Complications of heart disease
Complications of heart disease
Complications of heart disease include:
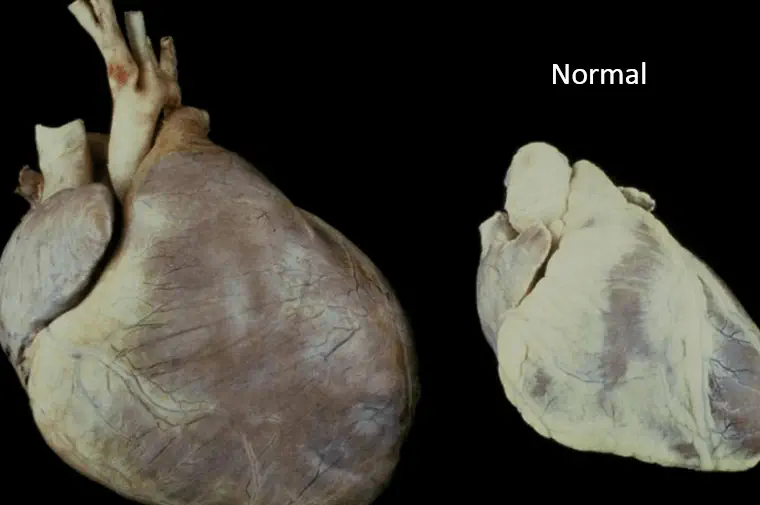
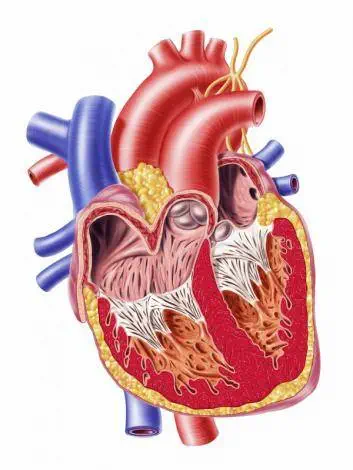
Heart failure. One of the most common complications of heart disease, heart failure occurs when your heart can’t pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs. Heart failure can result from many forms of heart disease, including heart defects, cardiovascular disease, valvular heart disease, heart infections or cardiomyopathy.
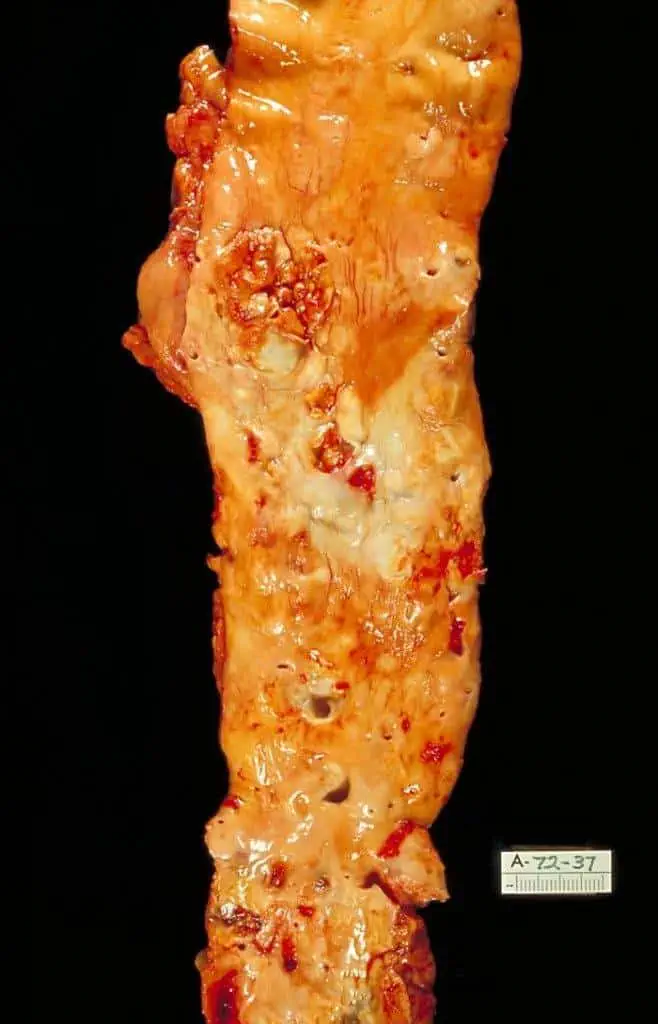
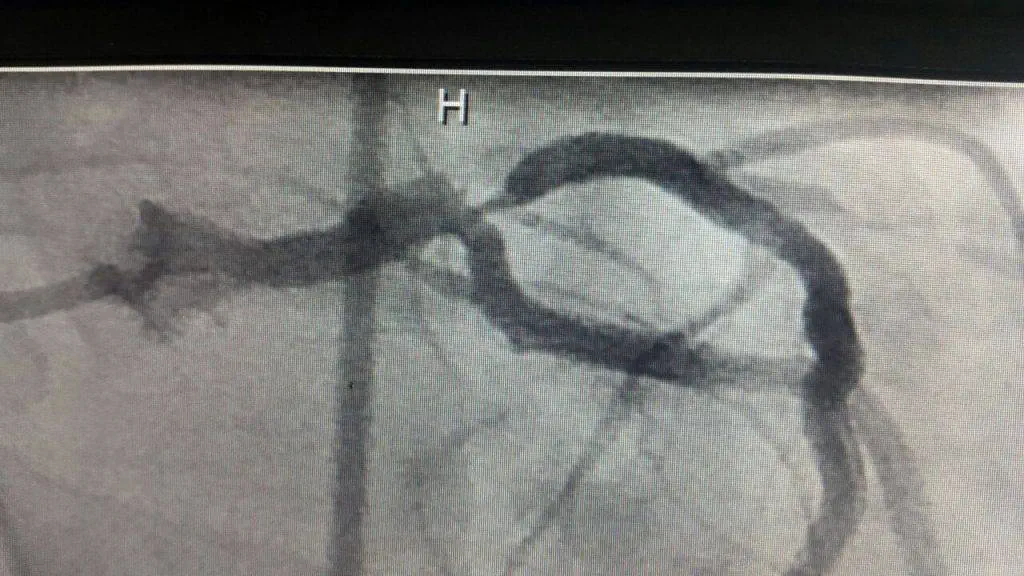
Heart attack. A blood clot blocking the blood flow through a blood vessel that feeds the heart causes a heart attack, possibly damaging or destroying a part of the heart muscle. Atherosclerosis can cause a heart attack.
Stroke. The risk factors that lead to cardiovascular disease also can lead to an ischemic stroke, which happens when the arteries to your brain are narrowed or blocked so that too little blood reaches your brain. A stroke is a medical emergency — brain tissue begins to die within just a few minutes of a stroke.
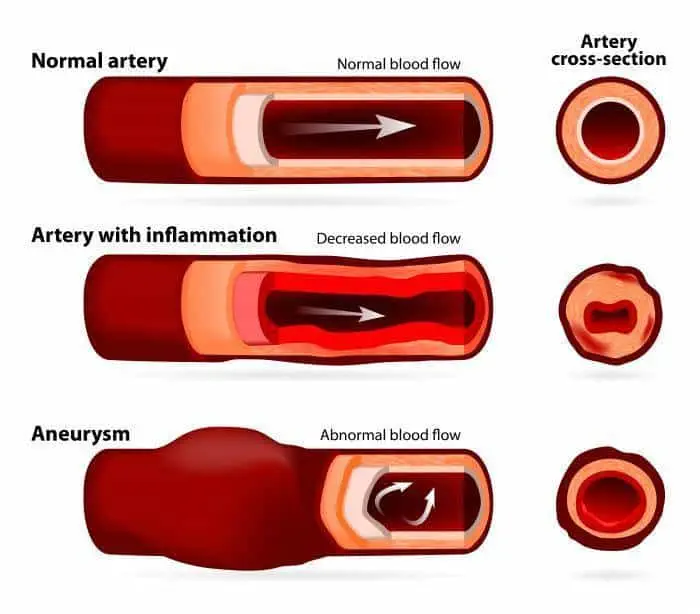
Aneurysm. A serious complication that can occur anywhere in your body, an aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of your artery. If an aneurysm bursts, you may face life-threatening internal bleeding.
Peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis also can lead to peripheral artery disease. When you develop peripheral artery disease, your extremities — usually your legs — don’t receive enough blood flow. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (claudication).
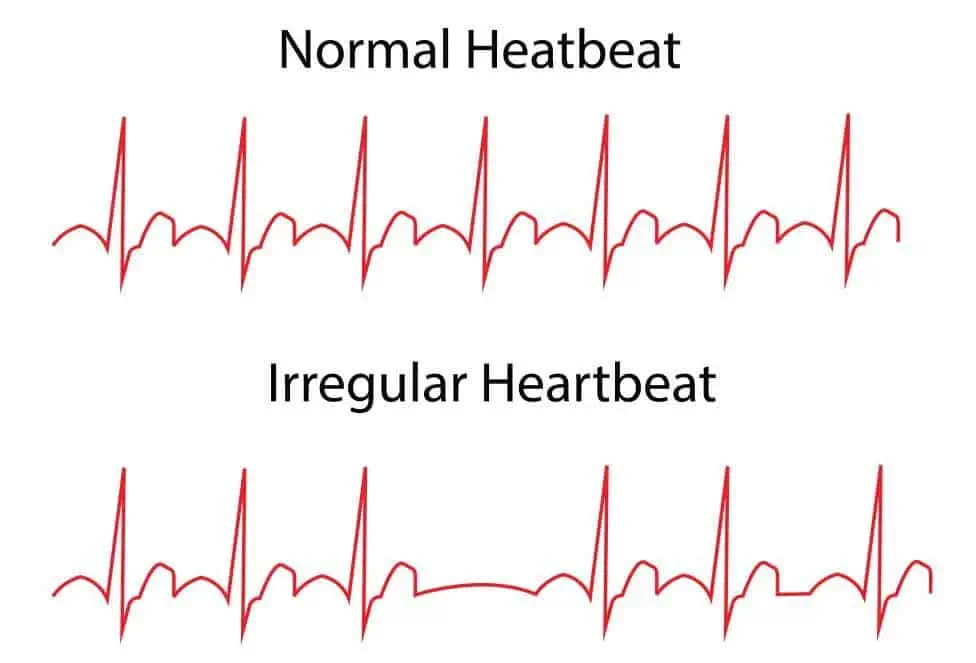
Sudden cardiac arrest. Sudden cardiac arrest is the sudden, unexpected loss of heart function, breathing and consciousness, often caused by an arrhythmia. Sudden cardiac arrest is a medical emergency. If not treated immediately, it is fatal, resulting in sudden cardiac death.